I2C Protocol
I2C stands for Inter-Integrated Circuit. It is a bus interface connection protocol incorporated into devices for serial communication. It was originally designed by Philips Semiconductor in 1982. Recently, it is a widely used protocol for short-distance communication. It is also known as Two Wired Interface(TWI).
Working of I2C Communication Protocol : It uses only 2 bi-directional open-drain lines for data communication called SDA and SCL. Both these lines are pulled high.
Serial Data (SDA) – Transfer of data takes place through this pin.
Serial Clock (SCL) – It carries the clock signal.
I2C operates in 2 modes
- Master mode
- Slave mode
Each data bit transferred on SDA line is synchronized by a high to the low pulse of each clock on the SCL line.
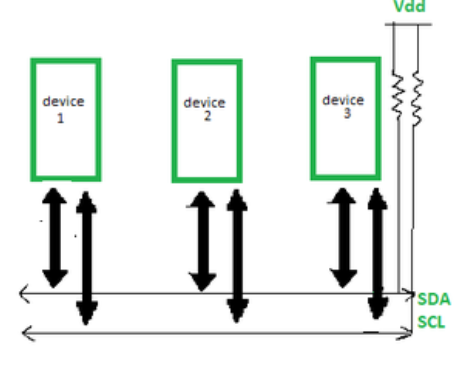
According to I2C protocols, the data line can not change when the clock line is high, it can change only when the clock line is low. The 2 lines are open drain, hence a pull-up resistor is required so that the lines are high since the devices on the I2C bus are active low.
The data is transmitted in the form of packets which comprises 9 bits. The sequence of these bits are –
- Start Condition – 1 bit
- Slave Address – 8 bit
- Acknowledge – 1 bit
